Enjoy 20% off sitewide except sets & gift cards. Code: MOTHER26
Melanin serves as your skin's natural defence system, determining your unique skin colour while acting as your body's built-in sunscreen. Understanding how this pigment functions and the factors that influence its production is essential for maintaining optimal skin health and addressing common pigmentation concerns.
Summary
Understanding skin pigmentation
Skin pigmentation occurs within the deepest layer of your epidermis, where specialized cells called melanocytes produce the protective pigment. This intricate system responds to various internal and external factors, adjusting production to meet your skin's changing needs.
Melanocytes synthesize and distribute pigment granules throughout surrounding skin cells, creating your skin tone while providing essential protection against environmental damage. When functioning optimally, this system maintains balanced pigmentation and supports overall skin health.
Melanin is the pigment responsible for skin color and plays a key role in the appearance of each freckle.
The two main types of skin pigment
Your skin contains two distinct types of this protective pigment. Eumelanin produces brown and black pigmentation, offering robust protection against UV radiation. This type is abundant in darker skin tones and provides superior photoprotective benefits.
Pheomelanin creates red and yellow pigmentation but provides less effective UV protection. The ratio between eumelanin and pheomelanin determines your natural skin colour and vulnerability to sun damage. Higher pheomelanin concentrations typically occur in fair skin, requiring additional protective measures.
How melanocytes create natural protection
When melanocytes detect UV exposure, they accelerate pigment production and transfer granules to surrounding cells. This creates a protective umbrella over skin cell nuclei, preventing DNA damage that could lead to premature ageing or skin concerns.
The process involves converting the amino acid tyrosine into pigment compounds through complex enzymatic reactions. This allows your skin to adapt its protection level based on environmental conditions, creating tanned skin during sun exposure while providing ongoing defence.
Where this pigment is found in your body
This protective compound exists throughout various body parts, each serving specific protective functions:
Hair follicles: determines hair colour and provides UV protection,
Eyes: found in the iris, contributing to eye colour while filtering harmful light,
Deeper skin layers: present in the dermis for continued protection as surface pigmentation changes,
Internal organs: provides antioxidant protection in brain and other tissues.
What does melanin do for your skin
This essential pigment serves multiple protective functions beyond determining skin colour, acting as a comprehensive defence system against environmental stressors.
Natural UV defence system
This pigment absorbs up to 99.9% of UV radiation, transforming potentially damaging light energy into harmless heat. This prevents free radical formation that could cause cellular damage, making it remarkably more effective than synthetic sunscreens at the cellular level.
However, understanding how SPF works to complement your skin's natural protection is crucial for comprehensive sun safety. This protection is crucial for preventing photoageing, which manifests as wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. Adequate pigment levels significantly reduce visible sun damage while preserving skin's youthful appearance.
Temperature regulation and skin barrier protection
Melanin influences how your skin absorbs and reflects light, contributing to temperature regulation. Darker pigmentation helps absorb heat in cooler environments while protecting against overheating in intense sunlight.
The pigment supports skin barrier integrity by protecting cellular structures responsible for maintaining hydration and preventing environmental irritants from penetrating skin. This function is essential for healthy, resilient skin.
The link between pigmentation and skin health
Balanced pigment production directly correlates with skin health, influencing protective capacity, appearance, and resilience. Optimal function maintains even pigmentation while providing adequate environmental protection, supporting healthy cellular turnover and preventing dark spot formation.
Disruptions in pigment production often signal underlying skin health issues or responses to stress, hormonal changes, or environmental damage.
Factors that influence pigment production
Understanding what affects pigment production helps you make informed skincare and lifestyle decisions.
Genetic factors and skin colour
Your genetic makeup determines baseline pigment production and skin colour. Inherited variations in production genes influence your natural skin tone and environmental response patterns, setting your skin's protective capacity foundation.
Genetics also determine susceptibility to pigmentation concerns like melasma, age spots, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. While unchangeable, understanding inherited tendencies helps develop appropriate prevention strategies.
Sun exposure and increased production
UV radiation is the most significant trigger for increased pigment production. When melanocytes detect UV exposure, they accelerate synthesis to create the familiar tanning effect while simultaneously boosting your skin's protective capacity. This natural response raises an important question for sun-conscious individuals: can you tan with sunscreen on? The answer lies in understanding how controlled UV exposure allows gradual pigment development while maintaining proper protection.
However, excessive sun exposure can disrupt these normal production patterns, causing uneven pigmentation and dark spot formation. Chronic exposure leads to photodamage that creates irregular pigmentation and premature ageing, highlighting the importance of balanced sun exposure practices.
Age-related changes in pigmentation
Ageing naturally alters pigment production patterns, often decreasing overall levels while developing concentrated dark spots. Melanocyte number and activity gradually decline, reducing natural protective capacity and increasing sun damage vulnerability.
Hormonal changes, particularly during menopause, significantly impact production, increasing susceptibility to melasma and hormonally-influenced pigmentation concerns.
Common pigmentation concerns
Imbalances in pigment production create various skin concerns affecting appearance and health.
Excess production and dark patches
Hyperpigmentation occurs when skin areas produce excess pigment, creating dark patches. Common forms include:
Age spots: UV-induced concentrated pigmentation,
Melasma: hormonal patches, typically facial,
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: following acne or injury,
Solar lentigines: sun-damage related spots.
These develop gradually from hormonal fluctuations, sun exposure, or skin inflammation. Early intervention with appropriate ingredients and sun protection prevents worsening.
Low production and skin vulnerability
Hypopigmentation creates lighter-than-normal skin areas lacking adequate UV protection. Conditions like vitiligo cause complete pigmentation loss, while other factors create subtle lightening that compromises natural defences.
Reduced pigment areas require additional protection to prevent burning and long-term damage, making comprehensive sun protection essential.
Lifestyle factors for healthy pigmentation
Supporting healthy pigment production involves practices that nourish skin while protecting from stressors:
Antioxidant-rich nutrition: foods high in vitamins C, E, and beta-carotene support protective processes,
Adequate hydration: maintains skin barrier protecting melanocytes,
Stress management: chronic stress triggers hormonal imbalances affecting production,
Regular exercise and sleep: support hormonal balance necessary for healthy patterns.
Your Caudalie routine for a healthy pigmentation
A balanced pigmentation requires comprehensive treatment and protection approaches using scientifically-formulated solutions.
Addressing sun spots and uneven pigmentation
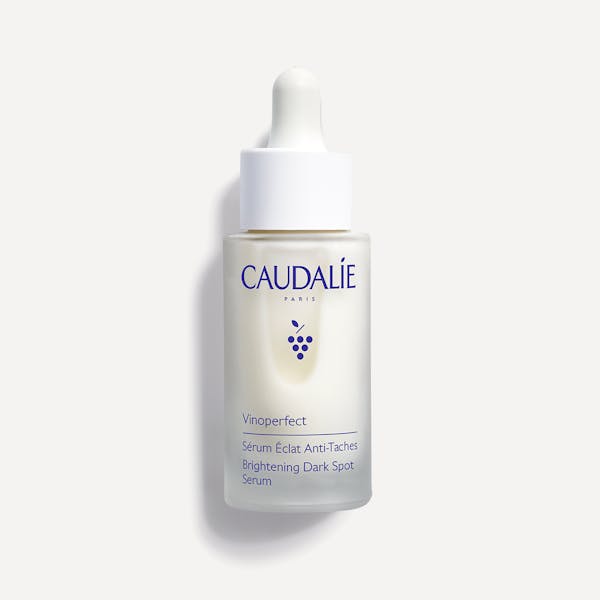
The Dark Spot Serum for Radiance features Viniferine, proven 62 times more effective than vitamin C at addressing dark spots, combined with olive squalane for hydration. This treatment gently inhibits excess melanin production while supporting healthy cell turnover, gradually lightening existing spots and preventing new concerns.
Vinosun Protect: a comprehensive approach to sun protection
Caudalie's Vinosun Protect collection provides optimal protection while caring for your skin and the environment. Thanks to a combination of organic filters, these products offer broad-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB rays, with the highest UVA protection PA++++(1). Dermatologically tested and suitable for sensitive skin, they are suitable for the whole family from 3 years old. Vegan, water-resistant, allergen-free, oxybenzone-free, octinoxate-free and alcohol-free, these products are also kind to the planet.
The CollagenSkinProtect™(2) antioxidant complex protects the skin's collagen and offers 100% protection against blue light(3) and 98% protection against infrared rays(3). All our products are formulated without nanoparticles, octocrylene or silicones.
Prevention remains the most effective pigmentation strategy. The Vinosun Protect range offers multiple high-protection formulations:
Sunscreen for Face SPF50+: this classic cream texture combines advanced sun protection. The lightweight formula provides reliable daily protection while supporting skin health through antioxidant action.
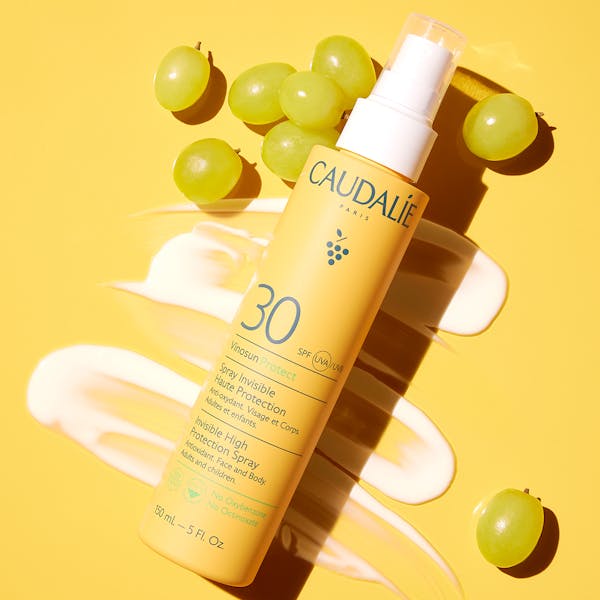
Invisible High Protection Spray SPF50: convenient spray format for easy reapplication throughout the day. This non-greasy Sunscreen SPF 50 absorbs quickly while providing comprehensive UVA and UVB protection, perfect for active lifestyles.
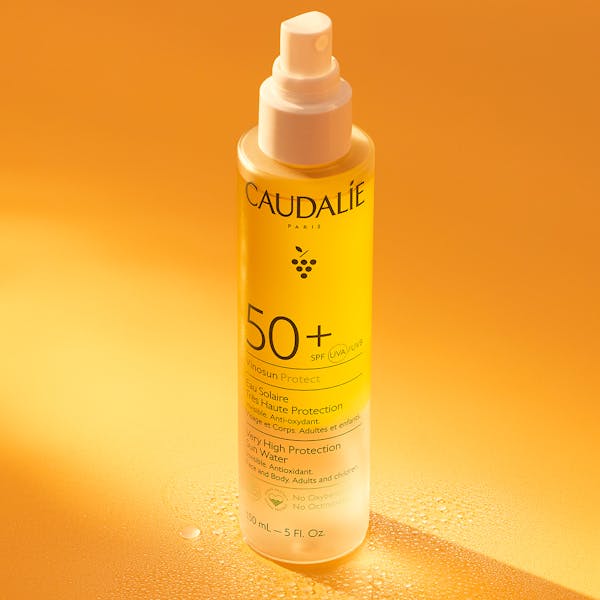
Very High Protection Sun Water: this innovative Sunscreen SPF50+ feels refreshing on skin while delivering identical high-level protection. The unique water-like texture makes sun protection enjoyable and ensures consistent application for optimal pigmentation protection.
Sunscreen Stick for Face SPF50: offering concentrated protection enriched with grape-seed oil and organic buriti oil for vulnerable areas. Ideal for protecting lips, moles, scars, and tattoos that require focused protection against UV-induced pigmentation changes.
Aloe Vera After Sun: this essential post-sun care features aloe vera extract, organic grape water, and coconut oil. The soothing formula maintains skin health after sun exposure while supporting natural repair processes that keep pigmentation balanced.
Understanding melanin's essential role in skin health and implementing comprehensive treatment and prevention strategies maintains balanced, healthy pigmentation that contributes to radiant, protected skin throughout your lifetime.
(1) Except for the Spray Invisible High Protection SPF30.
(2) Except for the Stick Invisible High Protection SPF50 and the After-Sun Repairing Lotion.
(3) Ex-vivo test.
LATEST BEAUTY NEWS